What makes a class or program rigorous? Is it harsh grading scales, a high workload, or high pressure? While some students, parents, and even instructors might believe so, there’s no evidence that these factors lead to better learning outcomes. In fact, the inverse can be true.
Instead, academic rigor refers to a learning environment with high expectations that provides students with the support they need to master their learning objectives and apply their learning in practice.
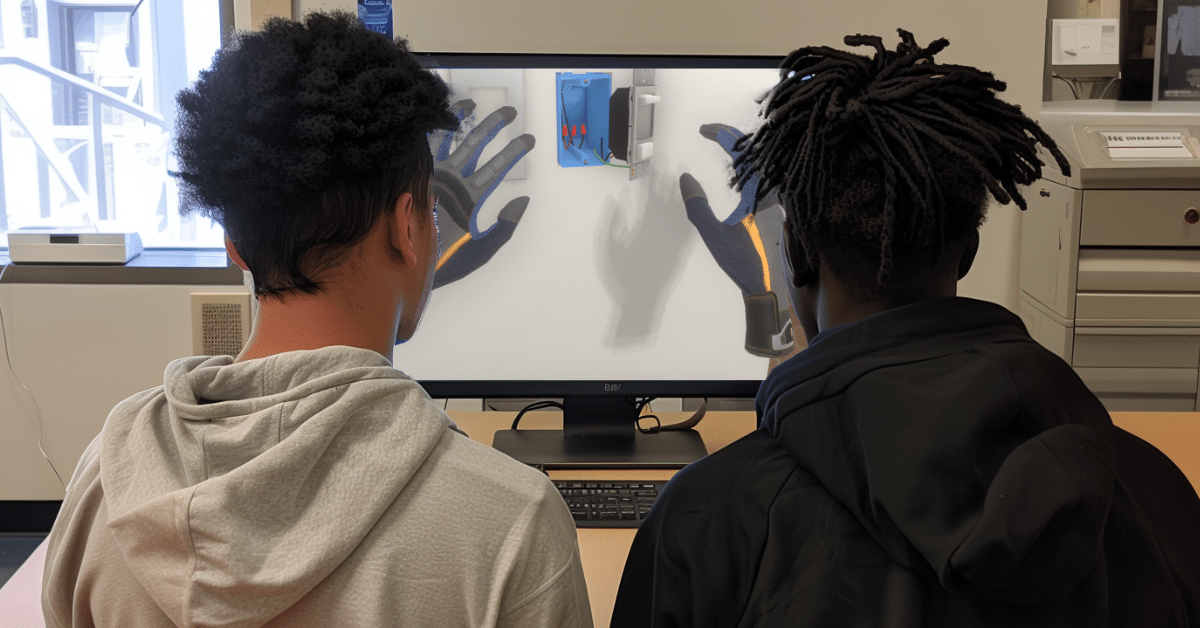
Academic rigor is equally important in CTE and practical skills training, despite historical misconceptions. Balancing foundational theory with practical training presents unique challenges due to resource constraints like lab space and funding. One way that instructors are meeting this challenge is through 3D simulations.
If you want to create an academically rigorous classroom in the skilled trades while engaging students on real-world problems, you’re in the right place. Let’s examine how you can use 3D simulations to create rigorous programs that engage all students, preparing them to tackle meaningful real-world challenges.
What Are 3D Simulations?
3D simulations are interactive virtual environments that allow users to explore and engage with virtual representations of objects, systems, or scenarios in three dimensions. In education, these immersive environments engage students on a multi-sensory level and make abstract concepts more tangible.
How Simulations Increase Academic Rigor Without Extra Effort
Some judge academic rigor by the input, such as the time and effort required, but this can be a faulty approach. Instead, you should measure academic rigor by a student’s output. Researchers Sara A. Wysea and Paula A. G. Sonerala describe academic rigor as learning meaningful content with higher-order thinking at the appropriate level for the context.
Based on this definition, here are four ways that 3D simulations support academic rigor in the classroom.
1. Critical Thinking
In a rigorous classroom, students need to learn how to think critically, engage with concepts that require deep thought and effort, and make connections between concepts.
To achieve this, they need to practice active learning where they interact with the course material. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy, this means not just recalling facts or understanding a theoretical concept. Students must also apply, analyze, evaluate, and create to master a subject.
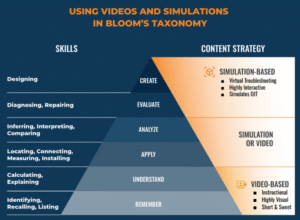
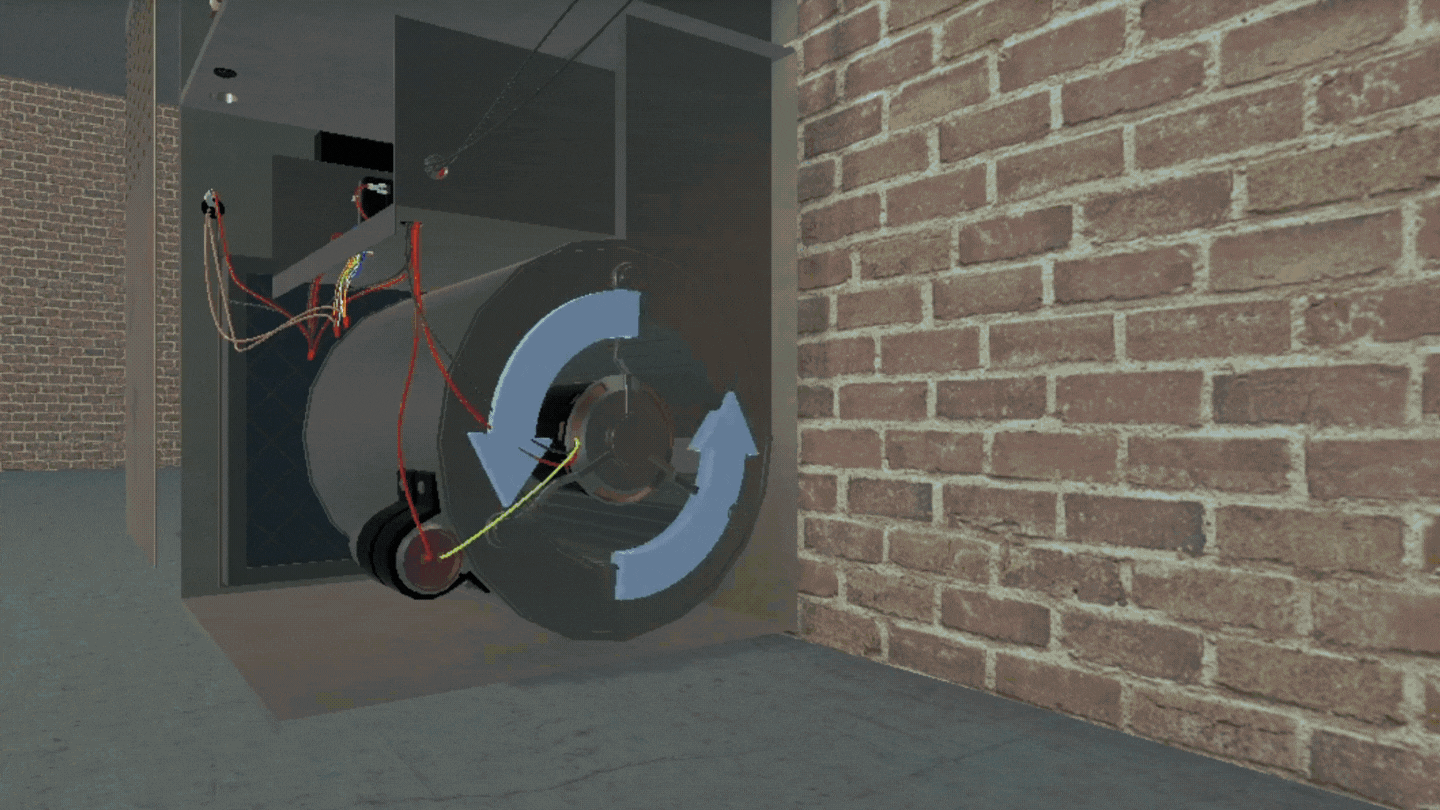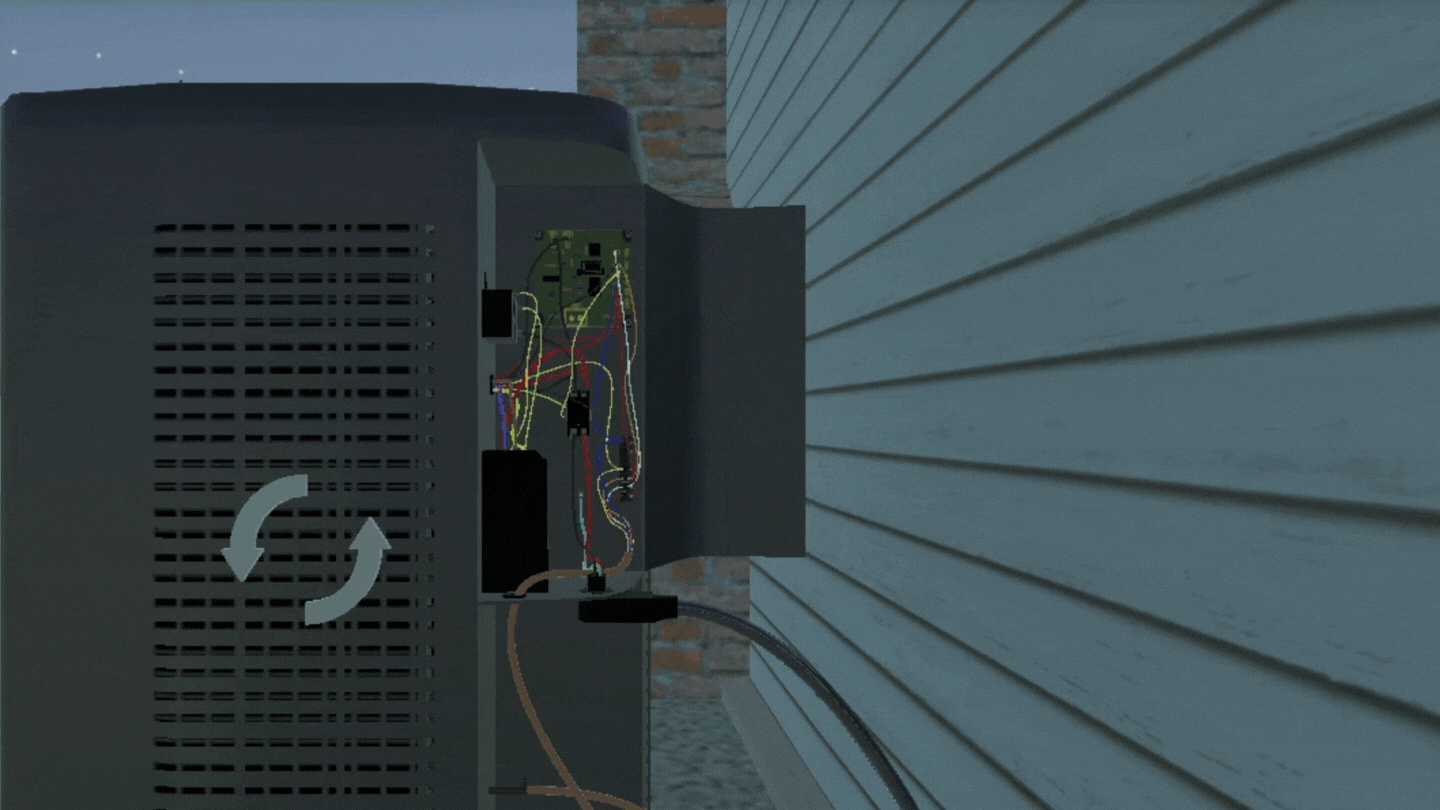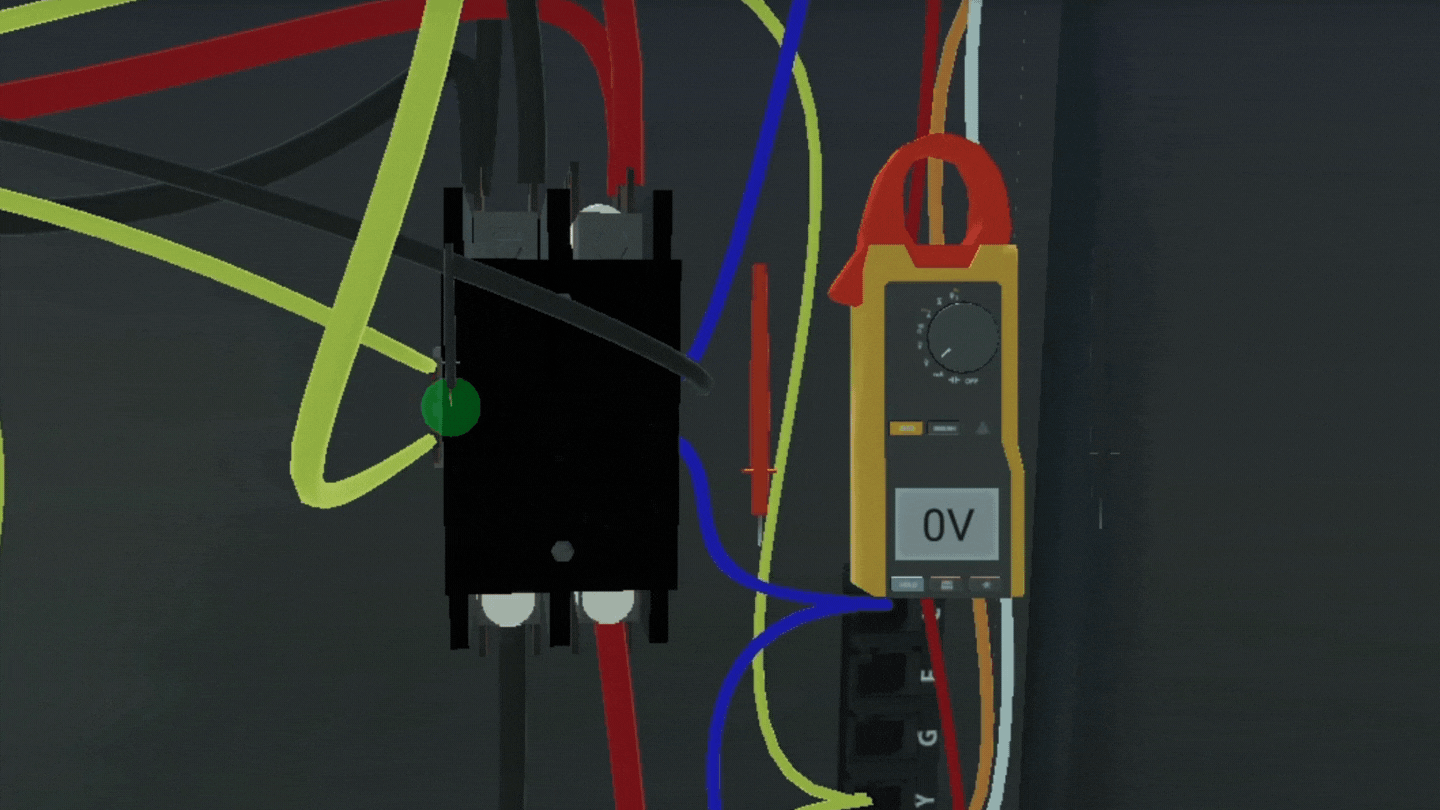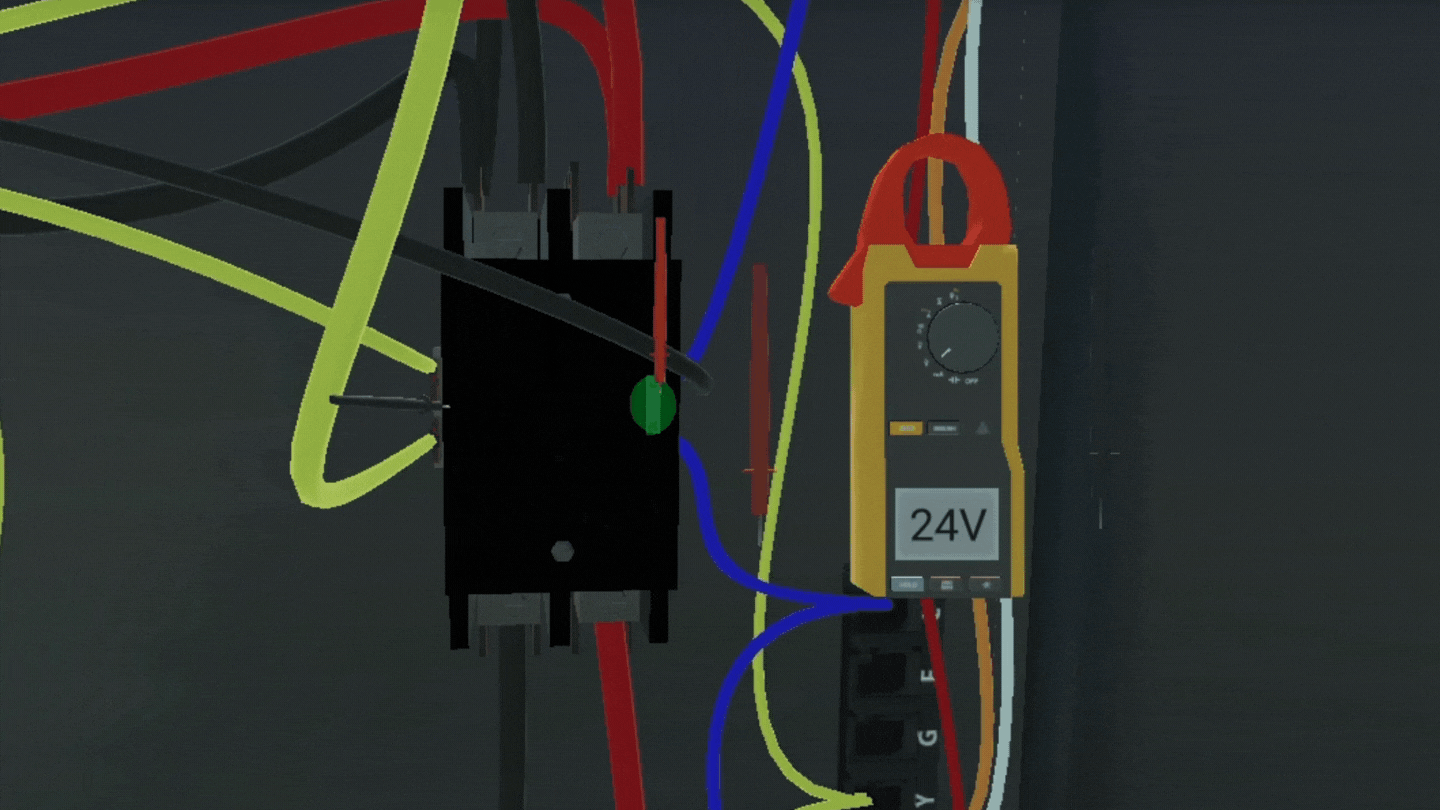
3D simulations position students for active learning by letting them apply concepts in a simulated environment, analyze physical environments with a hands-on approach, and evaluate their performance of a task with immediate feedback. The progressive approach of 3D simulations scaffolds critical thinking and troubleshooting, two of the most sought-after soft skills.
2. Self-Guided Learning
Many teachers already use differentiation in the classroom, allowing students to learn and progress according to their knowledge levels and abilities. While some argue that differentiation lowers academic standards by focusing on students who are progressing slower, this isn’t necessarily the case.
Tools designed for self-guided learning can increase rigor by giving individualized instruction and unlimited practice to each student. 3D simulations are a great example of this. An advanced student can complete lessons and assessments with little support, freeing instructors up to coach struggling students and help them reach high benchmarks alongside their peers.
3. Alignment with Industry Standards
One of the misconceptions about job-based training programs, particularly CTE, is that they aren’t rigorous because they teach technical and skills-based concepts instead of theory. Any engineer, doctor, or software developer could tell you this is a myth.
Alongside theory, hands-on skills aligned with industry standards are critical for developing graduates who will succeed in any career.
Studies show that students engage more with the course content when they can directly connect it to real-world problems. Working with industry partners to map curriculum to industry standards benefits employers and communities and sets students up for meaningful, lucrative careers.
4. Automatic Feedback
One limitation of the instructor-led classroom model is the time and effort it takes to provide individualized feedback. In a semester that’s only 18 weeks long, there is often a lag for grading, making it difficult for students to identify and address challenge areas without falling behind.
With 3D simulations, students complete interactive knowledge checks that measure their progress with instant feedback. This gives students self-awareness of their strengths and weaknesses. In platforms like Interplay Learning, leaderboards, badges, and goals incentivize students to improve every time they log in and try a new simulation.
Automated feedback with 3D simulations also reduces instructor time and workload, freeing them up for small group and individualized instruction.
Case Study: Indiana County Technical Center
One case study to look to is Indiana County Technology Center (ICTC), which successfully leveraged 3D simulations to increase academic rigor in its HVAC/R program.
Approach
ICTC integrated Interplay Learning’s 3D simulation courses into their curriculum, providing students with a clear and objective roadmap to practice their skills and competencies. The 3D simulations allowed students to reinforce classroom lectures and lab assignments through online, supplemental HVAC courses. This approach allowed ICTC to scale their programs in rural areas without sacrificing academic rigor.
Results
1. Enhanced Learning Retention
This multi-faceted approach combining theory, virtual practice, and hands-on application significantly improved learning retention rates and certification pass rates. 100% of graduates who took the state NOCTI exam passed with Advanced or Proficient overall scores, and 100% of students graduated with at least one industry-recognized certification.
2. Increased Post-Graduation Success
The rigorous training program, enhanced by 3D simulations, led to improved post-graduation outcomes:
- 81% of graduates continued in the HVAC field or pursued post-secondary education
- Students were better prepared for entry-level installer, maintenance, and service technician roles in residential and commercial fields
- Students felt more confident walking into real-world situations knowing they had the knowledge and skills necessary to be successful
Achieve Better Student Outcomes with Active Learning
Technical career fields including construction, electrical, plumbing, and HVAC are critical for the world in which we live. We need our best minds working on challenges like solar power and rebuilding infrastructure after a disaster. We owe all students a high-quality, high-expectations education— with the scaffolding they need to succeed.
Try out Interplay Academy’s 3D simulations! See our training in action.










